Abstract
Burkitt lymphoma is an aggressive type of non Hodgkin lymphoma, it is infrequent the presentation as appendicitis and is even more infrequent like appendicular peritonitis in adults. Clinic case: We reported a case of a 36-year-old man, who consulted with acute abdominal pain and fever. The physical examination showed abdominal resistance. An abdominal and pelvic computed tomography showed an increased in size appendix, perforated and a suspected tumoral mass. Surgery was performed, it was identified a tumoral mass dependent on the appendix, with compromise of cecum, subsequently a right hemicolectomy with primary anastomosis was performed. The histopathology showed Burkitt lymphoma. This article reports on a rare case of appendicular peritonitis in adults caused by Burkitt lymphoma and a review of the current evidence.
Keywords: Appendicular peritonitis; Burkitt lymphoma; Non Hodgkin lymphoma; Abdominal pain
Introduction
Non Hodgkin Lymphoma; (NL); is a heterogeneous group of pathologies of the immune system, with major prevalence in B cells [1]. The prevalence in E.E.U.U. is 19/100.000 persons [2]. Clinical manifestations include painless adenopathies, fever, weight loss, fatigue and itching [3].
Burkitt Lymphoma (BL); is a B cell lymphoma with high proliferation rate [4], is more common in kids and teenegers with a prevalence rate of 3-6 cases/100.000 persons [3-5]. Risk factors more relevant are immunosuppression, autoimmune disease, bacterial and viral infections [1].
Exist three types of BL:
- Endemic.
- Associated with immunodeficiency.
- Sporadic.
Endemic BL originates to areas where malaria is holoendemic [6] and is associated with infection with Epstein Barr virus [7]. Patients often present with an tumoral mass in jaw, orbit and abdomen [8]. Associated with immunodeficiency BL is associated with HIV infection, and affects marrow bone and gastrointestinal tract [9].
Sporadic BL typically occurs in children [10]. It affects more men than women. This type of BL usually occurs in the abdomen with compromise of ileocecal region, mimicking an acute appendix or an intestinal obstruction [3].
BL is diagnosed with clinical findings, CT and PET CT, biopsy, immunophenotype and molecular study [11].
Since BL is a rare medical condition in adults, we consulted the terms appendicular peritonitis and BL in PUBMED, SciELO, LILACS and Web of Knowledge in order to be able to write a case report and a review of the current evidence
Clinical Case
A 36-year-old male with a clinical history of dyslipidemia, operated testicular cancer. Non-smoker. Consulted in the emergency room with a three-day episode of abdominal pain, focused on right lower abdominal quadrant and fever.
During the physical examination; in the emergency department, vital signs showed: axillary temperature of 38°C, tachycardic, distended abdomen, tympanic, soft, depressible, pain in right lower abdominal quadrant and peri umbilical zone, and signs of peritoneal irritation.
Laboratory examinations showed elevation of C reactive protein and white blood cell count. Abdomen and pelvic CT scan with contrast reported (Figure 1): appendix with signs of increase of diameter, perforated, with free liquid in the pelvis, associated a mass in appendix zone, suspicious of malignant mass.
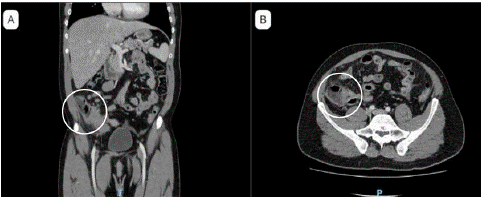
Figure 1: Abdominal and pelvis computed tomography with contrast (A) Appendix with signs of increase of size and free liquid in the pelvis (B) Mass in the cecal base, suspicious of malignant lesion.
Initial treatment included antibiotics, intravenous analgesia and preoperative preparation. The patient underwent surgery on the same day of his admission. Surgery was performed through exploratory laparotomy. It was identified peritoneal free fluid (purulent) with an increase in size of the appendix (with inflammatory and ischaemic signs), also had thickening of the appendicular base (Figure 2).
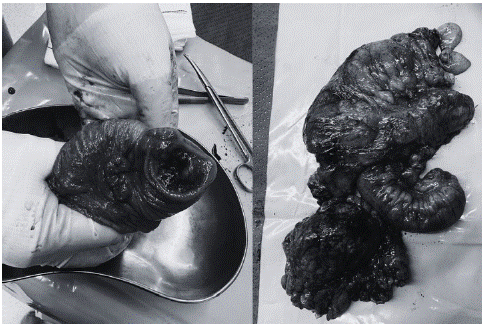
Figure 2: Surgical specimen.
In the mesocolon multiple lymph nodes larger than usual was identified in relation to ileocolic artery. We converted to a laparotomy for multiple adhesions, then right hemicolectomy and primary anastomosis was performed.
Without complications, he was discharged at six postoperative days. Histopathological analysis of the resected segment showed an appendix of 9,8 x 2,8 cm, perforated (2 centimeters) in the mid third. Cecum, cecal appendix and terminal ileum with BL, associated with mesenteric and pericolic nodule altered because of BL.
Immunohistochemistry showed: CD20, CD10, BCL6, KL67 positive and CD3, BCL2, CD30, c-MYC negative. Diagnosis: appendicular BL.
PET-CT (Figure 3) informed: hypermetabolic nodule close to sigmoid, and multiple bone involvement, in context of lymphoproliferative syndrome. We started chemotherapy with R-HyperCVAD (Cyclophosphamide, adriamycin, vincristine, dexamethasone), methotrexate and cytarabine. Four months later, he was controlled with radiologic exams. PET-CT (Figure 4): total metabolic response of bone and peritoneal compromise, without the appearance of new hyperenhancement focus. After a 7-month follow-up the patient recovered, with no recurrence.
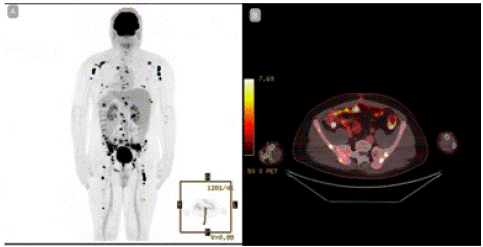
Figure 3: Positron emission tomography: hypermetabolic nodule close to sigmoid, and multiple bone involvement, in context of lymphoproliferative syndrome.
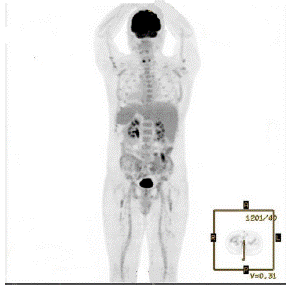
Figure 4: Positron emission tomography after chemotherapy: Bone and peritoneal metabolic with complete response.
Discussion
This case report shows an adult patient with a history of operated testicular cancer, presenting an acute appendicular peritonitis operation and subsequently pathological report showed appendicular BL.
BL is an aggressive B cell lymphoma [3], that compromises the gastrointestinal system in a 10-30% [12], is unusual the primary presentation in the appendix. Most of the BL cases are children (95%) [13].
In this case, the age and clinical presentation of the BL are infrequent; in an updated revision of the literature, we found 23 cases, of them 16 were children and 7 adults. In only two cases, a 81 years-old patient with prostatic cancer [14] and a 15 years-old patient [15], we found a clinical presentation and images suggestive of appendicular peritonitis.
Regarding the clinical presentation in adults [7] in our review, four presented with abdominal pain, 1 with peritonitis. Besides, two patients presented rectal bleeding and a unique case with abdominal mass and weight loss.
Almost all patients were studied with abdominal ultrasound and/or contrast abdominal CT. The principal finding was an inflamed and thickened appendix, associated with an increase of size lymph nodes. In this case, besides these findings, we found free liquid and cecal mass.
Biological markers shown indicative of BL ´s diagnosis: CD19, CD20, CD79A, PAX5, CD10, and BCL6; and negative ones: CD5, BCL2, and TdT [16]. Among the studied manuscripts, they have in common positivity for markers such as CD20, CD10, BCL6, and negativity for BCL2, CD30, CD3 [17-19], just like in the reported case. Our case stands out since the proto-oncogene C-MYC is negative, unlike other cases where it is positive. Regarding the follow-up, in the review of published cases of adult patients, follow-up is reported in only 2 cases, in which after surgery and chemotherapy are in good health at 10 months and 9 years.
Conclusion
In summary, this case, although exceptional, underlines the value of considering differential diagnoses to abdominal pain in the emergency setting, particularly in those with a history of oncological issues. The literature review emphasizes the rarity of this presentation, underscoring the need for further studies to better comprehend its management and long-term prognosis.
Author Statements
Acknowledgment
We extend our heartfelt gratitude to the dedicated team, including those pivotal to the patient's treatment. Immense gratitude to all contributors.
References
- Teras LR, DeSantis CE, Cerhan JR, Morton LM, Jemal A, Flowers CR. 2016 US lymphoid malignancy statistics by World Health Organization subtypes. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016; 66: 443-59.
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2022; 73.
- Roschewski M, Staudt LM, Wilson WH. Burkitt’s Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2022; 387: 1111-1122.
- Nguyen L, Papenhausen P, Shao H. The Role of c-MYC in B-Cell Lymphomas: Diagnostic and Molecular Aspects. Genes. 2017; 8: 116.
- Graham BS, Lynch DT. Burkitt Lymphoma. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2023.
- Kafuko GW, Burkitt DP. Burkitt’s lymphoma and malaria. Int J Cancer. 1970; 6: 1-9.
- de-Thé G, Geser A, Day NE, Tukei PM, Williams EH, et al. Epidemiological evidence for causal relationship between Epstein-Barr virus and Burkitt’s lymphoma from Ugandan prospective study. Nature. 1978; 274: 756-61.
- Burkitt D. A sarcoma involving the jaws in African children. Br J Surg. 1958; 46: 218-23.
- Gessese T, Asrie F, Mulatie Z. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Related Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Blood Lymphat Cancer. 2023; 13: 13-24.
- Kalisz K, Alessandrino F, Beck R, Smith D, Kikano E, Ramaiya NH, et al. An update on Burkitt lymphoma: a review of pathogenesis and multimodality imaging assessment of disease presentation, treatment response, and recurrence. Insights Imaging. 2019; 10: 56.
- Armitage JO, Gascoyne RD, Lunning MA, Cavalli F. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The Lancet. 2017; 390: 298–310.
- Lee W-K, Lau EWF, Duddalwar VA, Stanley AJ, Ho YY. Abdominal manifestations of extranodal lymphoma: spectrum of imaging findings. Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 191: 198–206.
- Saleh K, Michot JM, Camara-Clayette V, Vassetsky Y, Ribarg V. Burkitt and Burkitt-Like Lymphomas: a Systematic Review. Curr Oncol Rep. 2020; 22: 33.
- Myers EJA, Maldonado PDG, Rodríguez GM, et al. Apendicitis aguda como presentación inicial de linfoma de Burkitt. Acta Med. 2022; 20: 189-193.
- Shaw T, Cockrell H, Panchal R, Abraham A, Sawaya D. Burkitt Lymphoma Presenting as Perforated Appendicitis. The American Surgeon. 2022; 88: 547-548.
- Hummel M, Bentink S, Berger H, Klapper Wessendorf S, Barth TFE, et al. A biologic definition of Burkitt’s lymphoma from transcriptional and genomic profiling. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354: 2419-30.
- Nam S, Kang J, Choi SE, Kim YR, Baik SH, et al. Xanthogranulomatous Appendicitis Mimicking Residual Burkitt’s Lymphoma After Chemotherapy. Ann Coloproctol. 2016; 32: 83-6.
- Myers EJA, Jorge A, Maldonado PDG, Diana G, Rodríguez GM, et al. Apendicitis aguda como presentación inicial de linfoma de Burkitt. Acta Med. 2022; 20: 189-193.
- Oliveira C, Matos H, Serra P, Catarino R, Estevão A. Adult abdominal Burkitt lymphoma with isolated peritoneal involvement. J Radiol Case Rep. 2014; 8: 27-33.
